A turbocharger system dramatically improves internal combustion engine performance and efficiency by forcing more air into combustion chambers using exhaust gas power. This leads to increased fuel burning, higher power output, reduced nitrogen oxide emissions, and better fuel economy. Modern turbochargers feature advanced components like high-performance filters and efficient cooling systems to optimize airflow and further enhance engine performance.
The turbocharger system has emerged as a pivotal technology in the automotive industry, revolutionizing both engine performance and environmental sustainability. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of turbochargers on emissions and efficiency. We start with a fundamental overview, exploring the mechanics and components of these power enhancers. Subsequently, we analyze their effects on reducing harmful emissions like NOx and CO2 while enhancing combustion efficiency. Furthermore, we discuss the advantages and challenges related to efficiency boosts, including turbo lag and its implications for vehicle design.
Understanding Turbocharger Systems: A Basic Overview

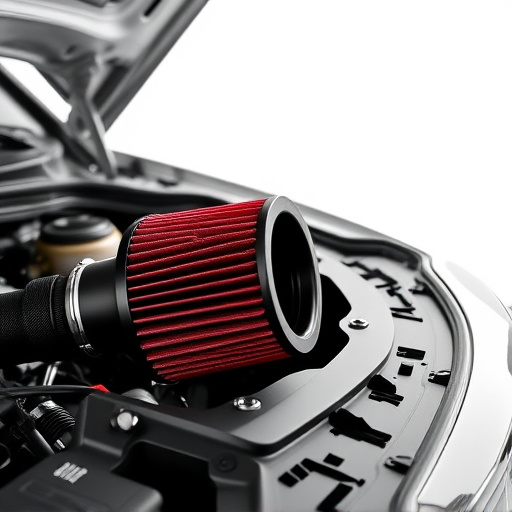
A turbocharger system is a powerful tool that enhances both the performance and efficiency of internal combustion engines. It works by forcing more air into the engine’s combustion chamber, allowing for increased fuel burning and thereby boosting power output. This process is achieved through a combination of a turbine and a compressor, which are driven by exhaust gases from the engine. The compressor draws in cold air from the front end of the vehicle, typically via a cold air intake, and pressures it before feeding it into the engine’s intake manifold.
This forced induction has significant benefits for emissions and efficiency. By increasing the amount of oxygen available for combustion, the engine can burn fuel more cleanly, leading to reduced emissions of pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx). Additionally, a turbocharger improves fuel economy by making the engine work more efficiently, as it can produce more power with less fuel input compared to naturally aspirated engines. This efficiency is further enhanced when combined with modern air intake systems designed for optimal airflow and performance.
– What is a turbocharger?

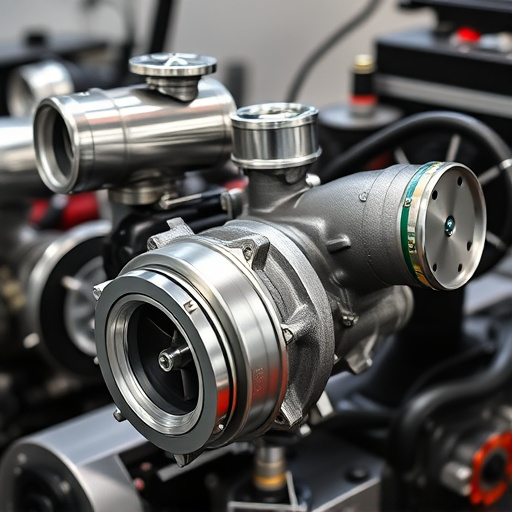
A turbocharger system is a mechanical device that forces more air into an engine’s combustion chamber, allowing for increased fuel burning and power output. It consists of a turbine, connected to a compressor via a shaft, which spins when exhaust gases from the engine pass through it. This motion drives the compressor, drawing in cold, dense air from the intake system before compressing it to increase its density and pressure. The enhanced air mixture results in more effective combustion, boosting the engine’s efficiency and performance.
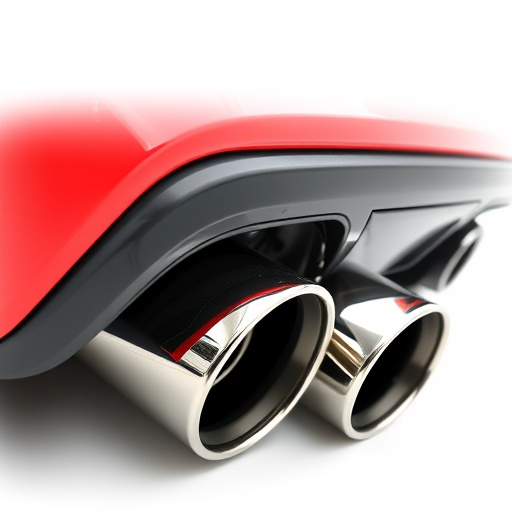
This technology is particularly beneficial for internal combustion engines, enhancing their power-to-weight ratio and improving fuel economy. In comparison to superchargers, turbochargers are more efficient as they rely on the engine’s exhaust flow, eliminating the need for a separate belt or gear drive. This design also promotes cleaner emissions, especially when coupled with advanced exhaust systems like cat back exhausts, by ensuring a well-controlled and precise air-fuel mixture. Additionally, modifications such as coilover kits and optimized air intake systems can further enhance the turbocharger’s performance capabilities.
– How does it work?

A turbocharger system is a powerful tool designed to enhance both the performance and efficiency of internal combustion engines. It operates by forcing more air into the engine than would be possible under normal atmospheric pressure, thereby increasing power output. At its core, a turbocharger consists of two main components: a compressor and a turbine. The compressor draws in ambient air and compresses it before feeding it into the engine’s intake manifold, boosting the air density and, consequently, the engine’s ability to burn fuel efficiently.
The turbine, powered by the exhaust gases from the engine, drives the compressor. This continuous cycle not only improves engine power but also reduces the time it takes for the combustion process. Additionally, modern turbocharger systems are often equipped with advanced cooling mechanisms and performance air filters to maintain optimal operating temperatures while enhancing filtration capabilities. Furthermore, efficient exhaust systems and exhaust mufflers can help reduce noise levels and further improve overall engine performance.
In conclusion, the turbocharger system has emerged as a pivotal technology for enhancing both vehicle performance and efficiency while reducing emissions. By compressing air to increase fuel combustion, it delivers powerful engine outputs with improved torque response. Simultaneously, this system contributes to environmental sustainability by optimizing fuel efficiency and minimizing harmful exhaust emissions. As the automotive industry continues to focus on cleaner, more efficient powertrains, the turbocharger system remains a key enabler in achieving these goals.